Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy is present at the birth of the Infant. A mother may notice excessive amniotic fluid or polyhydraminos. The mother may also notice less fetal movements than is normal. The baby is born sometimes prematurely. It is a disease that will cause multiple symptoms in the baby. The link to the baby is the mother in almost all cases. For instance, out of 118 cases only 2 cases had any incident that the father was the carrier. However, Paternal transmission (by the father) is documented. (Paternal Transmission of Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy J Med Genet 1994;31518-520) It seems as though the mother somehow causes the disease in the severe form. Some researchers postulate that there does not seem to be a genetic reason for the severe problems that may be caused by the disorder. It may be that the Myotonic Dystrophy in the mother somehow causes the severe congenital form.
In Sweden there is identified two types of congenital myotonic dystrophy, severe and moderate. In the severe type there is a life threatening condition at birth. This seems to be associated with male children more than female. With the moderate type of congenital myotonic dystrophy there is no life threatening condition birth. This information is contained in several studies as well as confirmed by by Ekstrom at a recent conference. The severe type will generally have more symptoms and more severe symptoms of the disease.
Congential as well as juvenile and adolenscent myotonic dystrophy are hard to diagnosis and identify. Part of the reason for this is that the medical profession does not recongnize this disease as a separate and distinct disease. They symtoms of congenital myotonic dystrophy are separate and distinct from mytonic dystrophy type 1. Thus, its hard for parents to identify the disease that their child may have. For example mental retardation and autism spectrum disorder are not symtoms of myotonic dystrophy. But they are symtoms of the congential or juvenile forms of the disease.
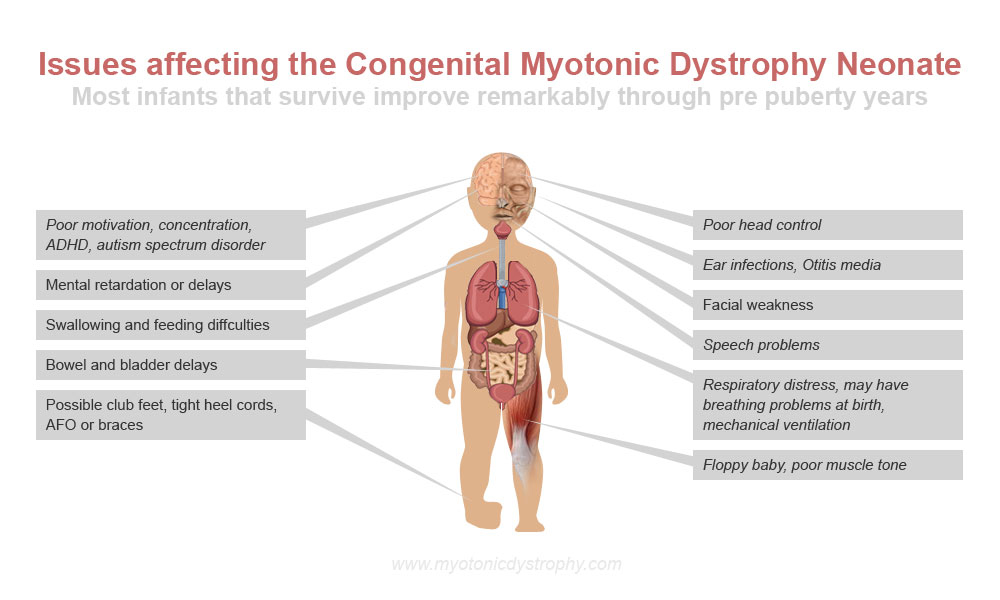
effects of Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy
Continue reading →
 Issues and problems with children that have congenital or juvenile myotonic dystrophy are many and hard to pin down. One of the most asked questions is about Autism and do children with Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy have Autism or Autism spectrum disorder. The basic criteria more are defined below for Autism like Features are before 3 years old the following 3 features are delayed or not present:
Issues and problems with children that have congenital or juvenile myotonic dystrophy are many and hard to pin down. One of the most asked questions is about Autism and do children with Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy have Autism or Autism spectrum disorder. The basic criteria more are defined below for Autism like Features are before 3 years old the following 3 features are delayed or not present:


