There are not many books about myotonic dystrophy. There is a fictional series about a skater that has myotonic dystrophy. I wrote a short book about the hopes and aspirations of my son “The boy who was President”. Now comes a great biography about a family with Myotonic Dystrophy. A must read for all with the disease. Here’s a short introduction:
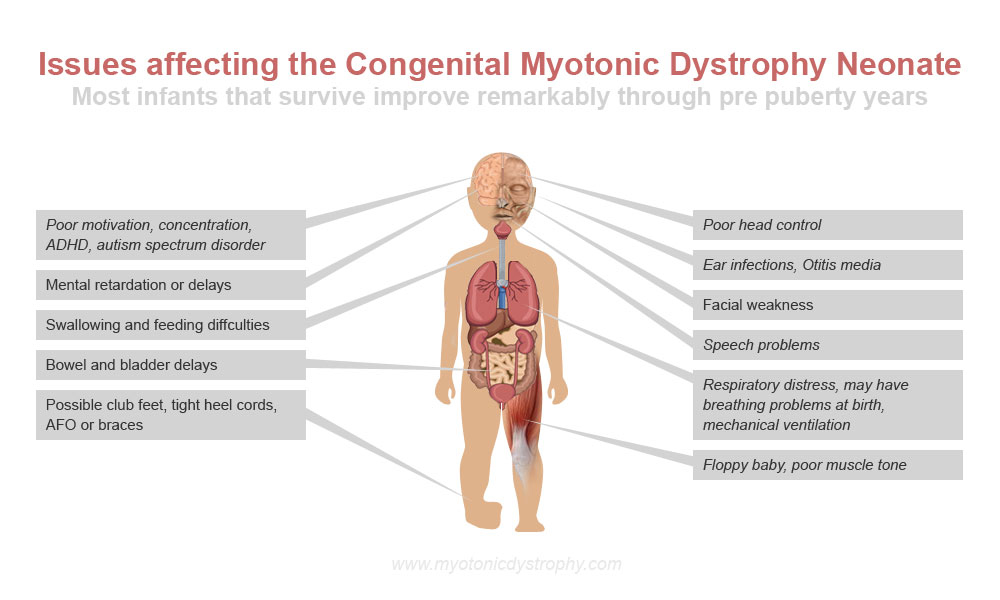
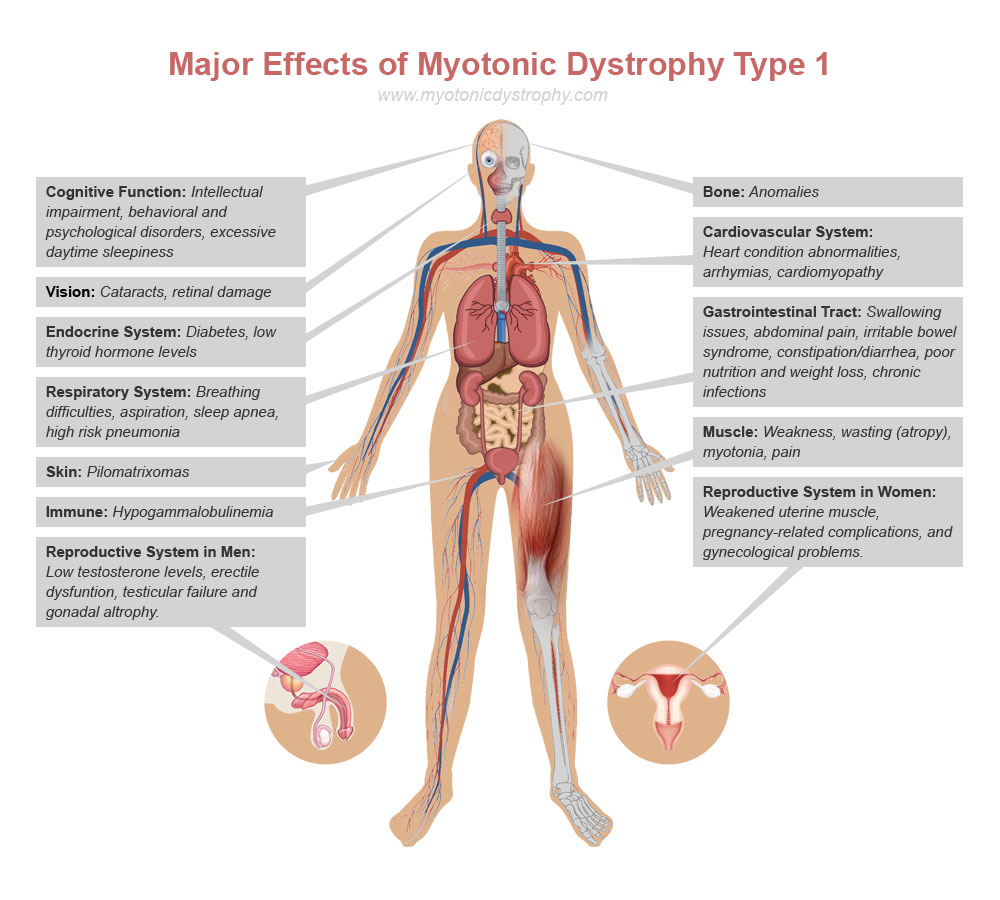
As a young girl, my constant goal was to help my brother, Dustin, walk. Dustin’s limits were hard to gauge because he constantly surpassed expectations. He was born with congenital myotonic dystrophy and expected to die, then to live three months, then three years. Instead, he gained strength and capabilities until age 13, when he had a simple cold and just did not wake up from his nap. His body became too much for the largest muscle in his body, his heart.
While Dustin was alive, I threw quarters in wells, prayed every night, and practiced with him every day after he had surgery and got corrective braces. I would stretch my brother’s legs, rotate his ankles, do resistance exercises and help him practice standing. At age 12, I thought willpower was so strong that, through perseverance and dedication, I could will my brother to walk.
Three years older than my brother, I grew up doing adult caretaking tasks. Through the years, I would change thousands of diapers, brush Dustin’s teeth, lift him into bed, administer nebulizer treatments, clean his feeding tube, watch him when both my parents had to work, bathe him, unload his wheelchair from the bus and play with him. Most things I did for my brother were helpful, but with my conceptions about willpower and Dustin walking, I pushed my brother past his comfort level more than once and caused more pain than progress. For me, a healthy sibling, willpower was a tool to push past obstacles. However, the same view I took of my young healthy body proved detrimental to my brother’s and caused him pain.